Focus on tool design and R & D
Precision cutting tools from Germanymanufacturer
+86 133-9231-4699
Focus on tool design and R & D
+86 133-9231-4699
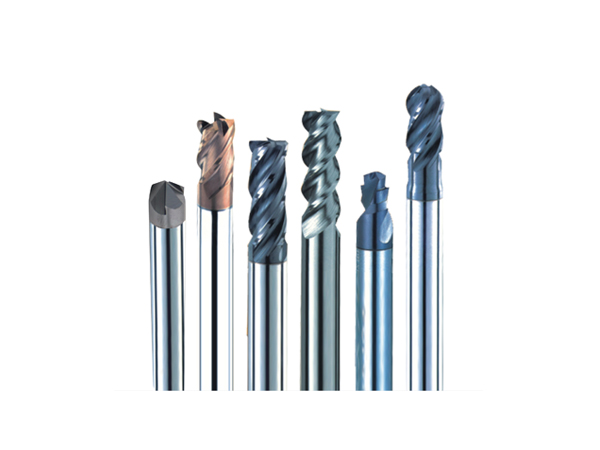

Undercutting various workpiece materials.
Although we always hope to have both high hardness to ensure the wear resistance of the tool, and high toughness to prevent the tool from chipping, the current technological development has not found such a superior performance tool material. You can't have both in the bear's paw. Therefore, we will choose more suitable tool materials in practice according to the needs: the toughness of the tool material is given priority when roughing: the hardness of the tool material is given priority when finishing. Of course, people are also looking forward to processing with ultra-high cutting speeds to obtain better results. The following is a brief introduction to common workpiece materials and related conditions of tools.
1. Aluminum alloy
1.1 Free-cutting aluminum alloy
This material is widely used in the aerospace industry. The applicable knives are K10, K20, PCD, the cutting speed is 2000-4000m/min, the feed rate is 3-12m/min, and the rake angle of the tool is 12°-18 °, the clearance angle is 10°~18°, and the blade inclination angle can reach 25°.
1.2 Cast aluminum alloy
Cast aluminum alloys use different tools according to their Si content. For cast aluminum alloys with Si content less than 12%, K10 and Si3N4 tools can be used. When Si content is greater than 12%, PKD (man-made diamond) can be used. ), PCD (polycrystalline diamond) and CVD diamond coated tools. For over-silicon aluminum alloy with Si content of 16%-18%, it is best to use PCD or CVD diamond-coated tools, the cutting speed can be 1100m/min, and the feed rate is 0.125mm/r.
2, cast iron
For castings, when the cutting speed is greater than 350m/min, it is called high-speed machining, and the cutting speed has a greater impact on the selection of tools. When the cutting speed is lower than 750m/min, coated cemented carbide and cermet can be selected: when the cutting speed is 510~2000m/min, the Si3N4 ceramic tool can be selected; when the cutting speed is 2000~4500m/min, CBN can be used Tool. The metallographic structure of the casting has a certain influence on the selection of high-speed cutting tools. For castings that are mainly pearlite, CBN or Si3N4 can be used when the cutting speed is greater than 500m/min. When ferrite is the mainstay, due to diffusion wear The reason is that the tool wear is serious, so CBN should not be used, but ceramic tools should be used. If the binder phase is metallic Co, the average grain size is 3μm, and the BZN6000 with a CBN content greater than 90%-95% is suitable for processing gray cast iron with high ferrite content when V=700m/min. The binder phase is ceramic (AlN+AlB2), the average grain size is 10μm, and the CBN content of Amborite inserts is 90%-95%. When processing gray cast iron with high pearlite content, when the cutting speed is less than 1100m/min, As the cutting speed increases, the tool life also increases.
3, ordinary steel
Cutting speed has a great influence on the surface quality of steel. According to research, the best cutting speed is 500~800m/min. At present, coated carbide, cermet, non-metal ceramic, and CBN tools can all be used as tool materials for high-speed cutting steel parts. Among them, the coated cemented carbide can be used as cutting fluid. The wear resistance of TiN coated tools produced by PVD coating method is better than that of coated tools produced by CVD coating method, because the former can maintain the shape of the cutting edge well, so that the machined parts can obtain higher precision and surface quality. . Cermet cutting tools currently occupy a large market share. The cermet based on TiC-Ni-Mo has good chemical stability, but has poor bending strength and thermal conductivity. It is suitable for small feeds with cutting speeds of 400-800m/min. Fine machining of small depth of cut: using TiCN as the matrix, the cermet with less molybdenum and more tungsten in the binder combines the strength and wear resistance, and TiN is used to increase the toughness of the cermet. The cutting depth of the processed steel or cast iron can be Up to 2~3mm.

4. High hardness steel
High-speed cutting tools of high-hardness steel (HRC40~70) can use cermet, ceramics, TiC-coated cemented carbide, PCBN, etc. The cermet can be made of TiC and TiN. Its hardness and fracture toughness are roughly equivalent to those of cemented carbide, but the thermal conductivity is less than 1/1O of cemented carbide, and it has excellent oxidation resistance and adhesion resistance. And abrasion resistance. In addition, it has good mechanical properties at high temperatures and low affinity with steel, making it suitable for medium and high speed (around 200m/min) die steel SKD processing. Cermet is especially suitable for grooving. Ceramic tools can be used to cut workpiece materials with a hardness of 63HRC. If the workpiece is quenched and then cut, "cutting instead of grinding" can be realized. When cutting 45 steel with a quenching hardness of 48~58HRC, the cutting speed can be 150~18Om/min, the feed rate is 0.3~0.4min/r, and the cutting depth can be 2~4mm. Al203-TiC ceramic tools with a particle size of 1μm and a TiC content of 20% to 30% can be used to process high-hardness steels with high spalling resistance when the cutting speed is about 100m/min. When the cutting speed is higher than 1000m/min, PCBN is the best tool material, and PCBN tools with CBN content greater than 90% are suitable for processing hardened tool steel (such as 55HRC H13 tool steel).
5. High temperature nickel-based alloy
Inconel 718 nickel-based alloy is a typical difficult-to-machine material. It has high high temperature strength, dynamic shear strength, low thermal diffusion coefficient, and work hardening easily during cutting, which will lead to high temperature and wear in the cutting area of the tool Speed up. When cutting this alloy at high speed, ceramic and CBN tools are mainly used. Silicon carbide whisker-reinforced alumina ceramics can obtain longer tool life at 100~300m/min. When the cutting speed is higher than 500m/min, the wear of TiC alumina ceramics is small, while at 100~300m/min The notch wear is relatively large. Silicon nitride ceramics (Si3N4) can also be used for the processing of Inconel 718 alloy. It is generally believed that the best cutting conditions for SiC whisker-enhanced ceramic processing Inconel 718 are: cutting speed 700m/min, depth of cut 1 to 2 mm, and feed rate 0.1 to 0.18 mm/z. Sialon ceramics have high toughness and are suitable for cutting solution-treated Inconel718 (45HRC) alloys. Al203-SiC whisker-reinforced ceramics are suitable for processing nickel-based alloys with low hardness.
6, titanium alloy (Ti6Al6V2Sn)
Titanium alloy has high strength and impact toughness, and its hardness is slightly lower than Inconel 718, but its work hardening is very serious, so high temperature and severe tool wear occur during cutting. Experiments show that high-speed milling of titanium alloy with a carbide K10 two-edged helical milling cutter with a diameter of 10mm (helix angle of 30°) can achieve a satisfactory tool life, the cutting speed can be as high as 628m/min, and the feed per tooth is desirable O.06~0.12mm/z, the cutting speed of continuous high-speed turning of titanium alloy should not exceed 200m/min.
7. Composite materials
Advanced composite materials used in aerospace. In the past, cemented carbide and PCD were used. The cutting speed of cemented carbide was limited. However, at a high temperature above 900 ℃, the welding place between the PCD blade and the cemented carbide or high-speed steel body is melted. Ceramic tools can achieve high-speed cutting of about 300m/min.
High-speed cutting technology has become the mainstream of cutting processing, and speeding up its promotion and application will create huge economic benefits. High-speed cutting tool materials play a decisive role in the development and application of high-speed cutting technology. Four types of high-speed cutting tool materials, including superhard tool materials (PCD and CBN), ceramic tools, TiC(N)-based cemented carbide tools (cermets) and coated tools, have their own characteristics and application ranges, and they cooperate with each other. Compete with each other to promote the development and application of high-speed cutting technology.
Mobile QR code

Official account

Applet