Focus on tool design and R & D
Precision cutting tools from Germanymanufacturer
+86 133-9231-4699
Focus on tool design and R & D
+86 133-9231-4699
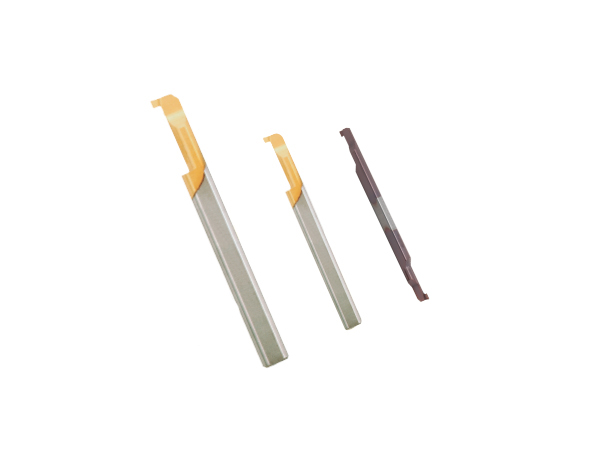

Diamond tools have extremely high hardness and wear resistance, low friction coefficient, high elastic modulus, high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion coefficient, and low affinity with non-ferrous metals. It can be used for precision processing of non-metallic hard and brittle materials such as graphite, high wear-resistant materials, composite materials, high silicon aluminum alloys and other tough non-ferrous metal materials. There are many types of diamond tools with significant performance differences. The structure, preparation methods and application fields of different types of diamond tools are quite different.
Natural diamond tools are mainly used for ultra-precision mirror processing of copper and copper alloys, gold, silver, rhodium and other precious non-ferrous metals, as well as special parts, such as video disks, optical plane mirrors, polygon mirrors and quadric mirrors. But its crystal anisotropy makes cutting tools expensive. The performance of PCD depends on the content of diamond grains and cobalt, and the tool life is 10 to 500 times that of cemented carbide (WC matrix) tools. It is mainly used for turning and processing various non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, magnesium and their alloys, cemented carbide, and non-metallic materials such as fiber plasticized materials with strong wear resistance, metal matrix composite materials, and wood. The cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut during cutting machining conditions depend on the material and hardness of the workpiece.
The performance and application of synthetic polycrystalline diamond composite (PDC) are close to PCD tools, mainly used in non-ferrous metals, cemented carbide, ceramics, non-metallic materials (plastics, hard rubber, carbon rods, wood, cement products, etc.) , Composite materials and other cutting processing, gradually replacing cemented carbide tools. Due to the residual bond metal and graphite in the diamond particles, the bond metal is distributed in agglomerated state or in the form of veins, which will reduce the wear resistance and life of the tool. In addition, there is a residual amount of solvent metal, and the solvent metal is in direct contact with the diamond surface. Reduce (PDC) oxidation resistance and tool heat resistance temperature, so the cutting performance of the tool is not stable enough. The preparation process of diamond thick film cutting tools is complicated because of the high interfacial energy between diamond and low melting point metals and their alloys.
Diamond is difficult to be wetted by common low melting point solder alloys. The weldability is extremely poor, and it is difficult to produce tools with complex geometric shapes, so TDF welding tools cannot be used in high-speed milling. Diamond-coated tools can be applied to high-speed machining. The reason is that in addition to the excellent mechanical properties of diamond-coated tools, the diamond coating process can prepare milling cutters with arbitrary complex shapes for high-speed machining such as aluminum-titanium alloy aerospace materials and difficult-to-machine non-metallic materials. Metal materials such as graphite electrodes, etc.
This article comes from: Dongguan Guorui Cutting Tools Co., Ltd.www.mjocut.com

Mobile QR code

Official account

Applet