Focus on tool design and R & D
Precision cutting tools from Germanymanufacturer
+86 133-9231-4699
Focus on tool design and R & D
+86 133-9231-4699
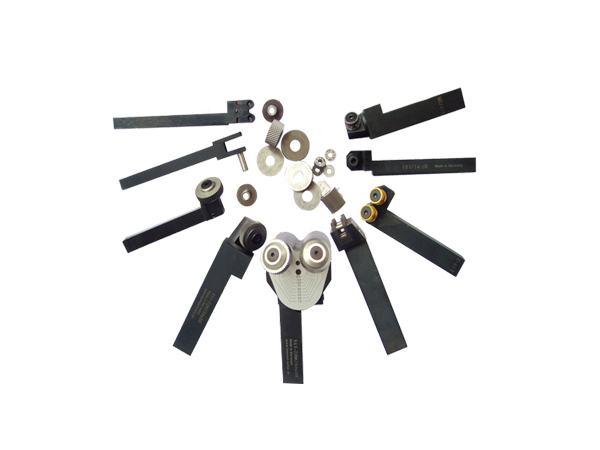

When placing alloy cutters, the firm bolts should be tightened in sequence and evenly. However, the bolts should not be tightened too tightly, otherwise it will lead to the absolute prohibition of the placement of the turning tool. The length of the cutter head protruding from the tool holder should be small even if it extends beyond the permanent robbery (L) 2H), it will cause the alloy cutter to vibrate, thereby destroying the alloy sheet, and otherwise, it will also reduce the cutting amount.
When external turning, the positioning of the turning tool should be exactly the center line of the tool tip, at least not higher than the diameter of the workpiece 0.01 mm, and when boring, the center should be accurately aligned. When placing a turning tool, it is better to use a thick shim than a few thin shim. Since the shim is not dense, vibrations will occur during the machining process, which will cause the carbide chip to collapse. When turning cast iron and bronze, the tool tip should be at the center line, at least not higher than the diameter of the workpiece 0.01mm, and when boring, the center should be accurately aligned. When placing a turning tool, it is better to use a thick shim than a few thin shim. Since the shim is not dense, vibrations will occur during the machining process, which will cause the carbide chip to collapse.
When turning cast iron, bronze and brass, the tip of the tool should be at the center line, while when turning steel, it can be slightly higher than the center line by 1 to 2 mm. The deflection of the machine tool spindle should not exceed 0.05 mm when machining steel parts, and should not exceed 0.10 mm when machining cast iron and other materials.

Mobile QR code

Official account

Applet